Stereocilia Ear Hair Cells | Damage for Inner Ear Hair Cells
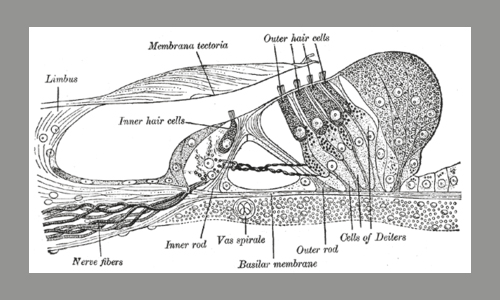
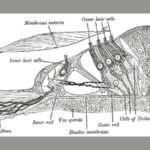
Stereocilia Ear Hair Cells:
The stereocilia or cilia are the hair-like projections on the top of the hair cells. In the inner ears are the mechanosensing organelles of hair cells, which reply to fluid waves in numerous types of animals for various tasks, including hearing and stability.
They are about 10- 15 micrometers in length and share some similar features of microvilli. The hair cells turn the liquid density and other mechanical stimuli into electric stimuli via the many microvilli that make up stereocilia rods.
Stereocilia exist in the auditory and vestibular system. The hair cells, and particularly the cilia, have their own mechanical activity. Damage to stereocilia resulting in the collapse, swelling or fusing of the cilia is likely to disengage or in some way compromise the tip links that normally connect the cilia of the hair cells.
This, in turn, compromises or cancels the chemical – the chemical electrical process needed for normal transduction, which then is likely to result in a sensorineural hearing loss. It is not just gross damage to the hair cell ( or its cilia) but also damages to the fine structures within the hair cell such as tip – links and cross-links that can be the basis for hearing loss.