What is a hearing aid ?

What is a Hearing Aid ?
A hearing aid is a small electronic device that is most commonly used by people suffering from hearing loss (mild/moderate/ severe / Profound). We wear the hearing aid in or behind our ear. It makes some sounds louder so that a person with hearing loss can listen, communicate, and participate more fully in daily activities. A hearing aid can help people hear more in both quiet and noisy situations. However, only about one out of five people who would benefit from a hearing aid actually uses one.
How a does a Hearing Aid help ?
Hearing aids are primarily useful in improving the hearing and speech comprehension of people who have hearing loss that results from damage to the small sensory cells in the inner ear, called hair cells. This type of hearing loss is called sensorineural hearing loss. The damage can occur as a result of disease, aging, or injury from noise or certain medicines.
A hearing aid magnifies sound vibrations entering the ear. Surviving hair cells detect the larger vibrations and convert them into neural signals that are passed along to the brain. The greater the damage to a person’s hair cells, the more severe the hearing loss, and the greater the hearing aid amplification needed to make up the difference. However, there are practical limits to the amount of amplification a hearing aid can provide. In addition, if the inner ear is too damaged, even large vibrations will not be converted into neural signals. In this situation, a hearing aid would be ineffective.
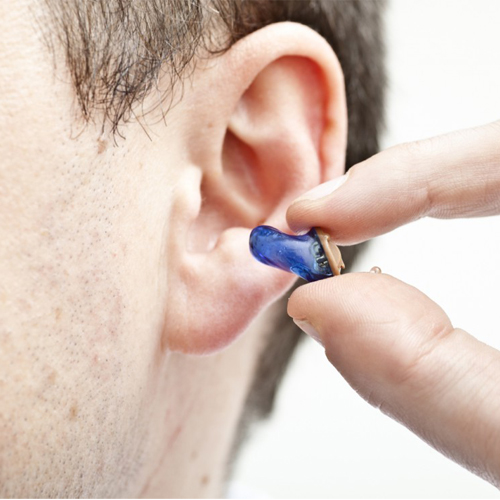
How does a Hearing Aid work ?
A hearing aid has three basic parts: a microphone, amplifier, and speaker. The hearing aid receives sound through a microphone, which converts the sound waves to electrical signals and sends them to an amplifier. The amplifier increases the power of the signals and then sends them to the ear through a speaker.
Benefits of using a Hearing Aid
Studies as well as experience show that hearing aids generally improve the quality of life and will help you:
- get a better relationship with your family
- feel better about yourself
- get better mental health
- improve your physical well being
- to concentrate better
- feel more independent and secure
- feel less tired or exhausted
- be more able to participate in social gatherings
- be able to increase your social contacts
- be able to do better in your job
Types of Hearing Aid
The two chief types of hearing aids are analog & digital.
Analog Hearing Aid
It converts sound waves into electrical signals, which are amplified.These hearing aids are usually pre programmed by the manufacturer to suit a certain degree of hearing loss. Analog aids usually are less expensive than digital aids.
Digital Hearing Aid
It converts sound waves into numerical codes, similar to the binary code of a computer, before amplifying them. Because the code also includes information about a sound’s pitch or loudness, the aid can be specially programmed to amplify some frequencies more than others. Digital circuitry gives an audiologist more flexibility in adjusting the aid to a user’s needs and to certain listening environments. These aids also can be programmed to focus on sounds coming from a specific direction.
Styles of Hearing Aid
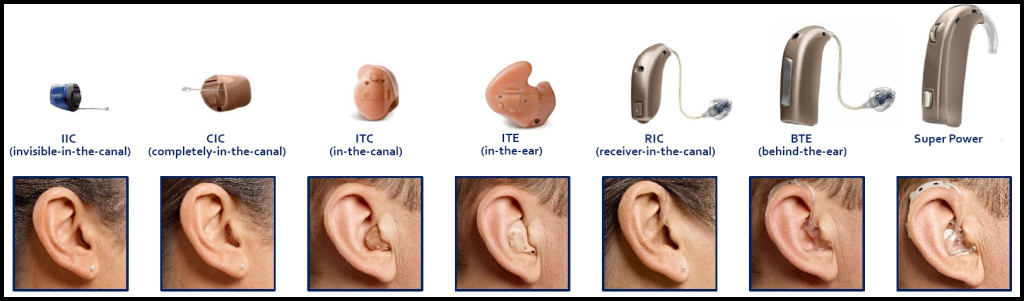
- Behind The Ear hearing aid (BTE)
- Mini- Behind The Ear hearing aid (mini-BTE)
- Receiver In the Canal hearing aid (RIC)
- In The Ear (ITE) hearing aid
- In The Canal (ITC) hearing aid
- Completely In the Canal (CIC) hearing aid
- Invisible In the Canal (IIC) hearing aid




