What is Hearing loss ?

What is Hearing Loss ?
Hearing loss or hearing impairment, is a condition when there is a problem with one or more parts of the ear or ears, the nerves coming from the ears, or the part of the brain that controls hearing. “Impairment” means something is not working correctly or in a way it should be. Generally the terms hearing impaired or hard of hearing denote the people who have relative insensitivity to sound in the speech frequencies. The severity of a hearing loss is categorized according to the increase in volume above the usual level necessary before the listener can detect it.
What causes Hearing loss ?
- Age
- Noise
- Genetic
- Perinatal problems
- Disorders
- Medications
- Chemicals
- Physical trauma

General Sings & Symptoms
- Difficulty using the telephone
- Loss of directionality of sound
- Difficulty in understanding speech, especially of women and children
- Difficulty in speech discrimination against background noise (cocktail party effect)
- Sounds or speech becoming dull, muffled or attenuated
- Need for increased volume on television, radio, music and other audio sources
- Pain or pressure in the ears
- A blocked feeling in the ear
- Hyperacusis, heightened sensitivity to certain volumes and frequencies of sound, sometimes resulting from “recruitment”
- Tinnitus, ringing, buzzing, hissing or other sounds in the ear when no external sound is present
- Vertigo and disequilibrium
- Tympanophonia, abnormal hearing of one’s own voice and respiratory sounds, usually as a result of a patulous eustachian tube or dehiscent superior semicircular canals
- disturbances of facial movement (indicating possible tumour or stroke)
Types of Hearing Loss
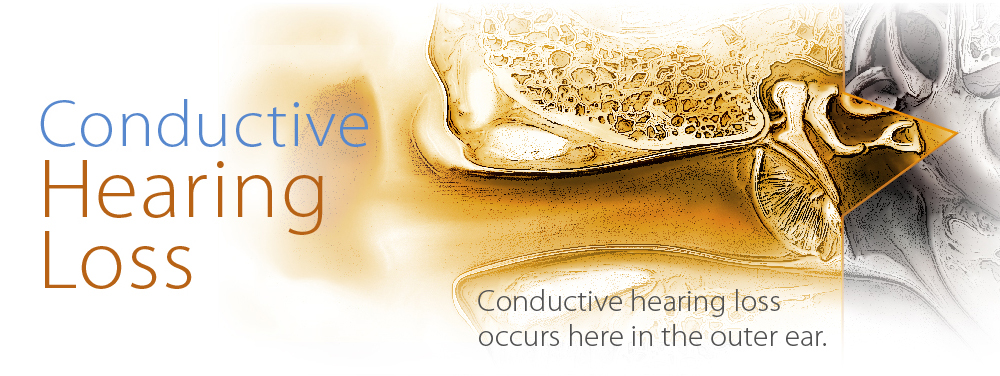
Conductive hearing loss
when hearing loss is due to problems with the ear canal, ear drum, or middle ear and its little bones (the malleus, incus, and stapes).
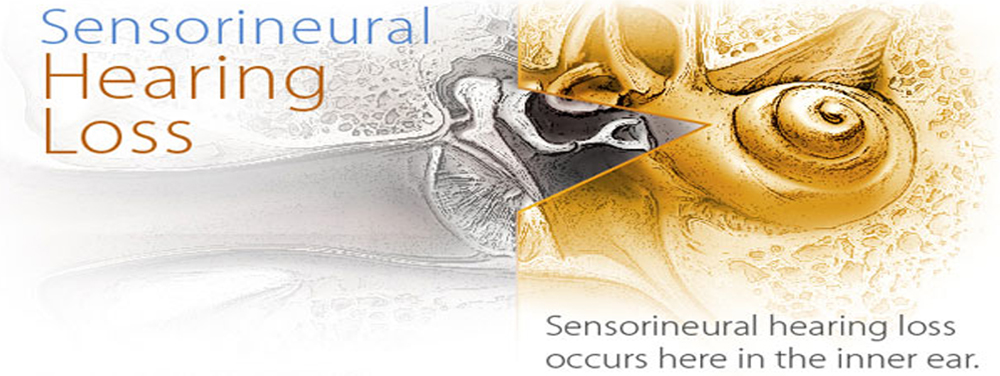
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL)
when hearing loss is due to problems of the inner ear, also known as nerve-related hearing loss.
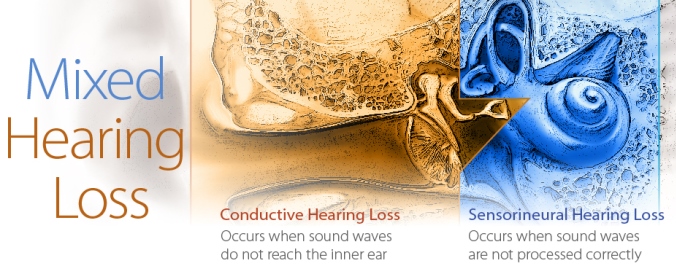
Mixed hearing loss
refers to a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. This means that there may be damage in the outer or middle ear and in the inner ear (cochlea) or auditory nerve.
Basic Methods to Prevent Hearing Loss
- By wearing Hearing Protectors in noisy environments
- Regulating excess noises in work place
- Regular screening for hearing loss
Treatment for Hearing Loss
Hearing aids,
are the devices that work by magnifying the sound vibrations in the ear so that one can understand what is being said around them. These include digital and analog versions.
Assistive Devices,
these are instruments used by individuals from hard of hearing to communicate with others in their daily lives. Eg., telephone typewriters, special software for instant messaging, Sound generators, etc.,
Surgical,
there is no any surgical treatments for hearing loss due to most common causes such as age, noise & genetic effects. Surgeries are preferred when following conditions exists: myringotomy, acoustic neuroma, stapedectomey etc., Cochlear implants improve outcomes in people with hearing loss in either one or both ears. They work by artificial stimulation of the cochlear nerve by providing an electric impulse substitution for the firing of hair cells. They are expensive, and require programming along with extensive training for effectiveness.
Bone anchored implants,
suitable for people who are unable to use hearing aids and for some levels of sensorineural hearing loss




